Understanding the Endocrine System
Have you ever wondered why you sometimes feel invincible, while other times you’re totally wiped out for no reason at all? Or why your mood can swing from happy to “meh” with seemingly little provocation? You might not realize it, but a lot of this comes down to the secretive, but incredibly powerful world of hormones and the endocrine system.
Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through your bloodstream, directing many of the body’s key functions. Think of them as the body’s internal communication system, ensuring that different parts of the body talk to each other in a way that helps keep everything running smoothly. But what happens when those hormones are out of whack? That’s when things can go haywire.
What is the Endocrine System?
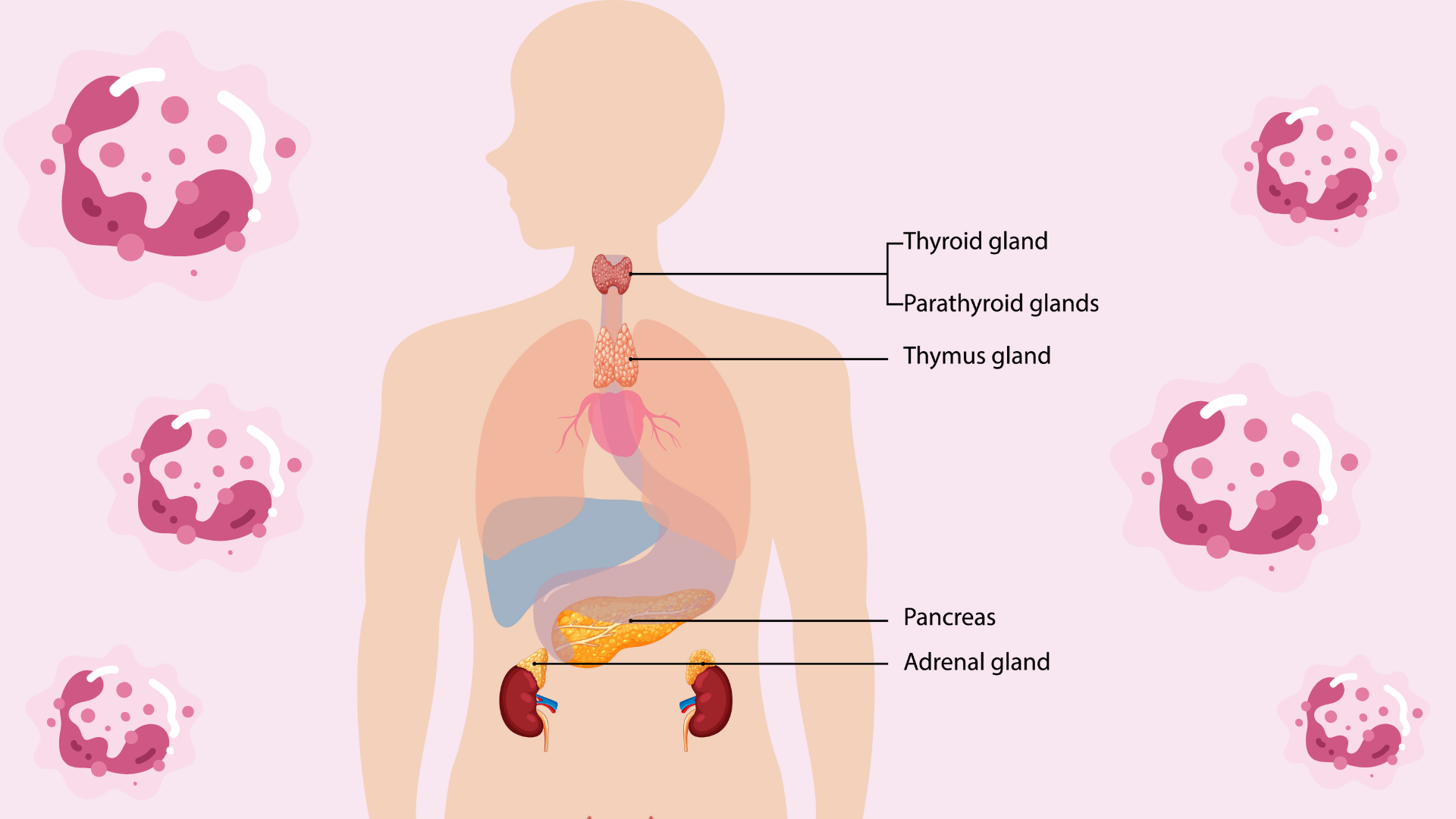
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and release hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones regulate essential functions like metabolism, growth and development, mood, sexual function, sleep, and more. Major glands in the endocrine system include:
- Pituitary Gland: Known as the “master gland,” it controls other glands and is responsible for growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
- Thyroid Gland: Regulates metabolism, energy, and mood.
- Adrenal Glands: Produce hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, which help manage stress and regulate metabolism.
- Pancreas: Controls blood sugar levels by producing insulin.
- Ovaries/Testes: Produce sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone), which influence sexual function and reproductive health.
- Pineal Gland: Produces melatonin, regulating sleep cycles.
The Importance of Balanced Hormones
Each hormone plays a crucial role in maintaining balance in the body, and even slight disruptions can lead to noticeable symptoms or health problems. Think of it like a symphony orchestra—each instrument (hormone) has a specific role to play. If one instrument is off-key, it can throw the entire performance out of whack.
Here’s how balanced hormones affect different functions in your body:
- Metabolism & Energy: Your thyroid hormones, especially thyroxine, help control your metabolism. If your thyroid is sluggish (hypothyroidism), you might feel tired, gain weight, or have trouble focusing. On the other hand, an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can leave you feeling jittery and cause unintended weight loss.
- Mood & Mental Health: Hormones like serotonin, dopamine, and cortisol have a huge impact on your mental well-being. Low levels of serotonin can lead to depression or anxiety, while high levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, can lead to irritability or a feeling of being “on edge.”
- Sleep Patterns: The pineal gland’s production of melatonin helps regulate your sleep-wake cycles. Disruptions in melatonin levels can lead to insomnia or poor sleep quality.
- Reproductive Health: Estrogen and progesterone control the menstrual cycle and pregnancy, while testosterone is important for sexual function and muscle mass in both men and women. Imbalances here can lead to fertility issues, low libido, or mood swings.
- Growth & Development: Growth hormone (GH) is key during childhood and adolescence to ensure proper physical development. Inadequate GH production can lead to growth delays, while too much can cause gigantism or acromegaly.
What Happens When Hormones Go Rogue?
Sometimes, your endocrine system gets a little out of sync, leading to hormone imbalances that can cause a range of health problems. These imbalances can occur due to factors like genetics, stress, diet, age, or even environmental toxins. Here’s a list of some common disorders and issues that disrupt hormonal balance:
1. Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
- Symptoms: Fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, depression, constipation, sensitivity to cold.
- Cause: Often caused by autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or iodine deficiency.
2. Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
- Symptoms: Weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, excessive sweating, tremors.
- Cause: Graves’ disease, thyroid nodules, or excessive iodine intake.
3. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Symptoms: Irregular periods, excess facial hair, acne, difficulty losing weight.
- Cause: Elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) and insulin resistance.
4. Adrenal Fatigue
- Symptoms: Chronic fatigue, difficulty waking up, salt cravings, irritability, difficulty concentrating.
- Cause: Chronic stress leading to overproduction of cortisol.
5. Diabetes (Type 1 & Type 2)
- Symptoms: Excessive thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, fatigue, slow healing of wounds.
- Cause: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder where the body attacks insulin-producing cells; Type 2 is often related to insulin resistance.
6. Cushing’s Syndrome
- Symptoms: Weight gain (especially around the face and abdomen), high blood pressure, mood swings, thin skin.
- Cause: Overproduction of cortisol, often due to tumors or prolonged steroid use.
7. Hypogonadism (Low Testosterone or Estrogen)
- Symptoms (Men): Low libido, erectile dysfunction, reduced muscle mass, fatigue.
- Symptoms (Women): Hot flashes, mood swings, irregular periods, bone density loss.
- Cause: Aging, injury, or disorders affecting the ovaries or testes.
8. Growth Hormone Deficiency
- Symptoms: Slow growth in children, increased body fat, decreased muscle mass, and poor bone density in adults.
- Cause: Pituitary gland dysfunction, tumors, or genetic conditions.
9. Hyperprolactinemia
- Symptoms: Unexplained breast milk production, missed periods, infertility.
- Cause: Elevated prolactin levels, often due to a pituitary tumor or medications.
10. Menopause
- Symptoms: Hot flashes, mood swings, vaginal dryness, sleep disturbances.
- Cause: Natural decline in estrogen production as women age.
How to Maintain Hormonal Balance
Maintaining a balanced endocrine system is essential for overall health, and the good news is that there are many ways you can support your body’s hormone health:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in whole foods, healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants supports optimal hormone function. Avoid processed foods and excess sugar, which can disrupt insulin balance.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps regulate insulin, cortisol, and growth hormones. Aim for a mix of cardio and strength training.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress leads to overproduction of cortisol, which can lead to a cascade of other hormonal issues. Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get Enough Sleep: Sleep is essential for maintaining hormone balance, especially melatonin, cortisol, and growth hormones. Aim for 7–9 hours of restful sleep each night.
- Avoid Endocrine Disruptors: Certain chemicals in the environment, like BPA and phthalates, can interfere with hormonal balance. Opt for natural cleaning products and avoid plastic containers for food storage.
- Consult Your Doctor: If you’re experiencing symptoms of hormonal imbalance, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. Blood tests can help identify imbalances, and your doctor can work with you to find the right treatment plan.
Final Thoughts
Your endocrine system is the unsung hero of your body, silently orchestrating a symphony of vital processes that keep you alive and thriving. By understanding the role hormones play in your health and the many factors that can disrupt this balance, you can take steps to maintain harmony within your body. Because when your hormones are in balance, everything else just seems to fall into place.
So, the next time you’re feeling a little off, remember—your hormones might just be trying to tell you something!
